Category: SOC - CyberTalents - Trend Micro
Agenda
- Cybersecurity Introduction
- SoC Arch
- Network Analysis
- Endpoints Analysis
- Web Analysis
- Email Analysis
- Log Analysis
- SIEM Solutions
- SIEM Use cases
- Digital Forensics & Incident response (DEIR)
Lesson 1: Introduction to Cybersecurity
Cyber Attacks
A cyber-attack is a threat that targets computer systems, infrastructures, computer networks, and/or personal computer devices. Cyber-attacks are occurring all the time. Cyber attackers use malicious code to alter other code, logic, or data on a computer system in order to disrupt service or commit cyber-crimes such as information or identity theft.

Laws & Legalese
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR- EU) & Sarbanes Oxley (USA) Law No. 175 of 2018 Regarding Anti-Cyber and Information Technology Crimes (Egypt).
According to article 14, individuals who gain access to or hack a website, private account, or prohibited information system, whether intentionally or unintentionally, may be penalized with imprisonment of no less than a year and/or a Fine OF EGP 50,OOO — 100,OOO. IF the hacking leads to the damage, erasure, altering, copying, or redistribution OF data or information, the term OF imprisonment would be For no less than two years.
Types of Common Attacks
- Zero-day Attack
- Malicious software
- Phishing
- Insider Attacks
- Data exfiltration
- Lateral Movement
- Denial of Service (DOS)
Zero Day Attacks

- A Zero-day Attack is one in which an attacker exploits a zero-day vulnerability unknown to developers to infiltrate a system with malware or spyware or gains unwanted access to personal user information or sensitive data.
- Once the vulnerability is discovered, developers must race to release a software patch to protect users before the attacker can compromise the system.
Malicious Software
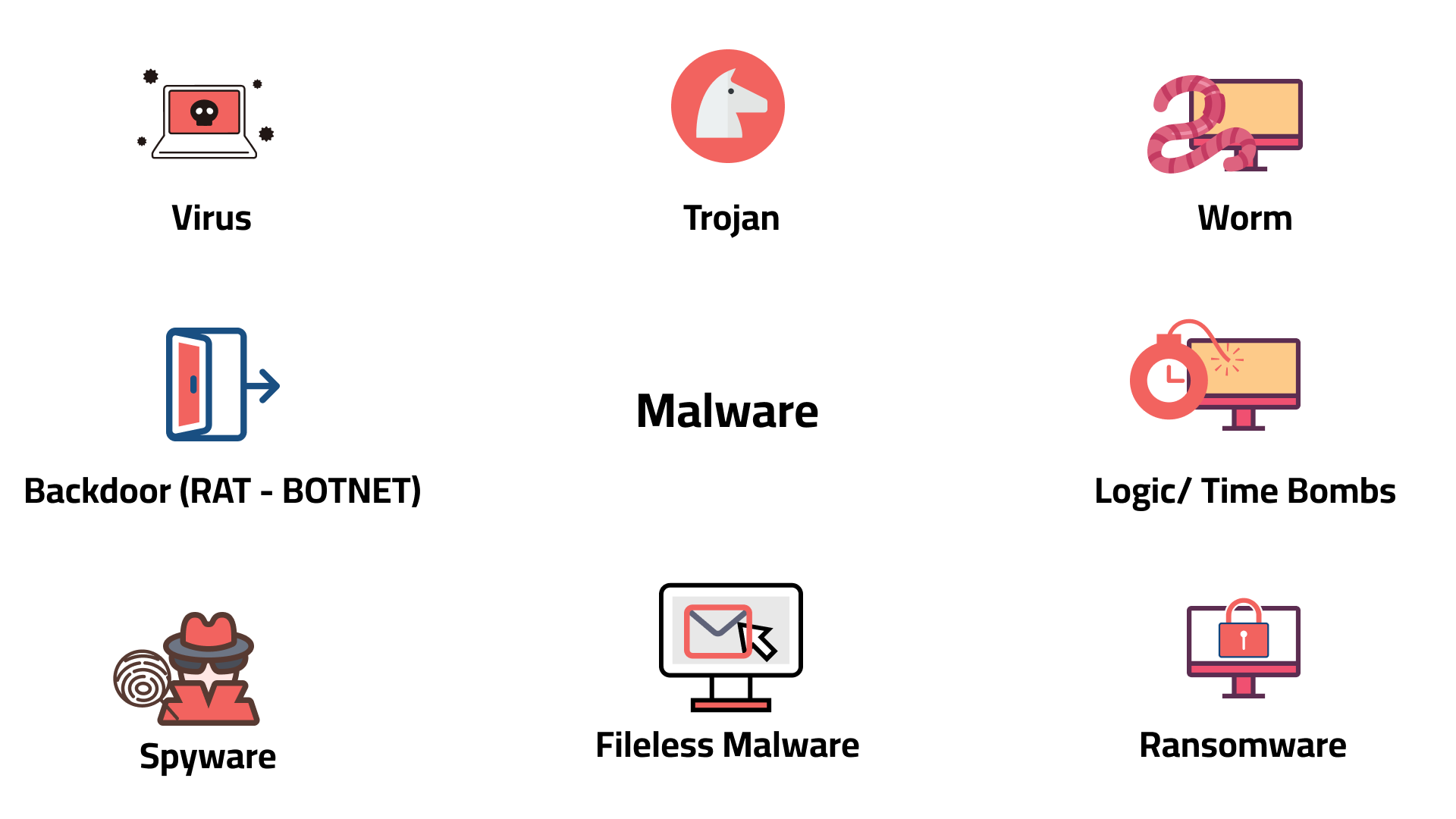
- Malicious software, known as Malware, is software designed to harm a computer or system. It’s introduced into a system in a number of ways. A user may download the executable file from a malicious site.
- The malware can arrive as a payload dropped or downloaded by other malware already introduced into the system.
Phishing
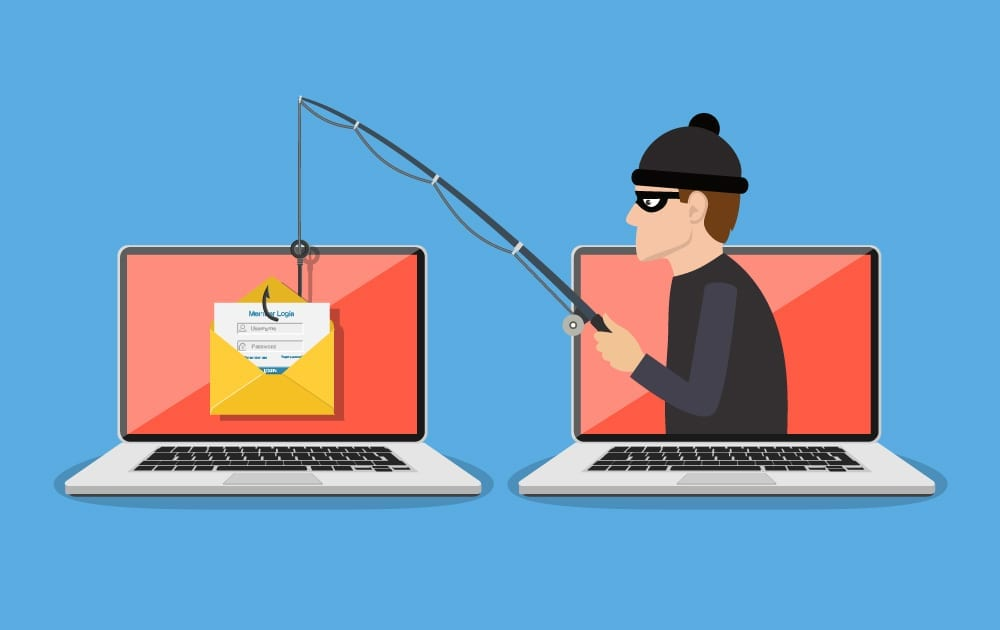

Phishing is a type of social engineering where an attacker sends a fraudulent (e.g., spoofed, fake, or otherwise deceptive) message designed to trick a person into revealing sensitive information to the attacker or to deploy malicious software on the victim’s infrastructure like ransomware (Wikipedia).
Insider attacks
- Insider attacks present some of the greatest threats to organizations. An insider threat is an attacker with access to network resources and sensitive data that steals or alters personal information or company secrets.
- Insider threats are often terminated employees with legitimate credentials. Insider attacks can also come from outside attackers using employee credentials to infiltrate the network.
Data Exfiltration

- Data exfiltration, also known as data theft or extrusion, is one of the greatest threats to organizations.
- Data exfiltration refers to the unauthorized transfer of sensitive data from a network to a location controlled by the attacker such as an external storage device, personal or competitor email account, or cloud storage site for the purpose of committing cyber crimes such as identity theft or corporate espionage.
| 📌Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions are security tools that help organizations to ensure that sensitive data such as Personally Identifiable Information (PII) or Intellectual Property (IP) does not get outside the corporate network or to a user without access. |
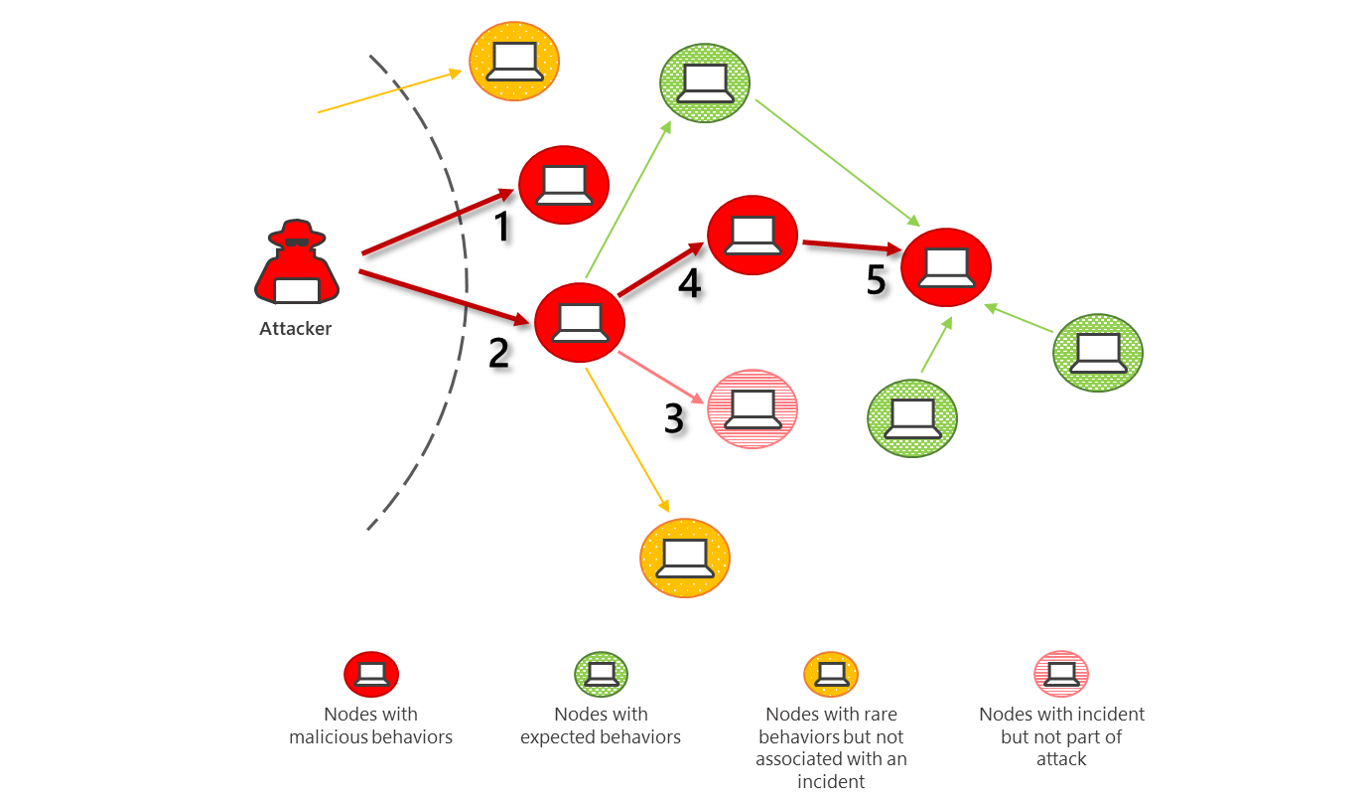
Lateral Movement
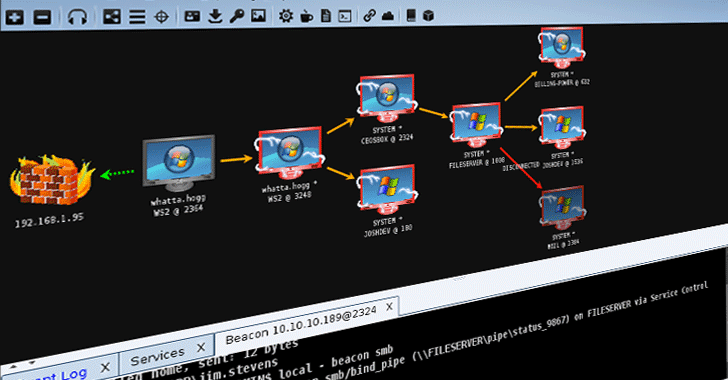
Lateral Movement is a strategic intrusion that spreads across a network compromising resources searching for key assets and sensitive data. Lateral movement is difficult to stop once the infection spreads from the initial infected resource to other resources on the network.
Denial of Service
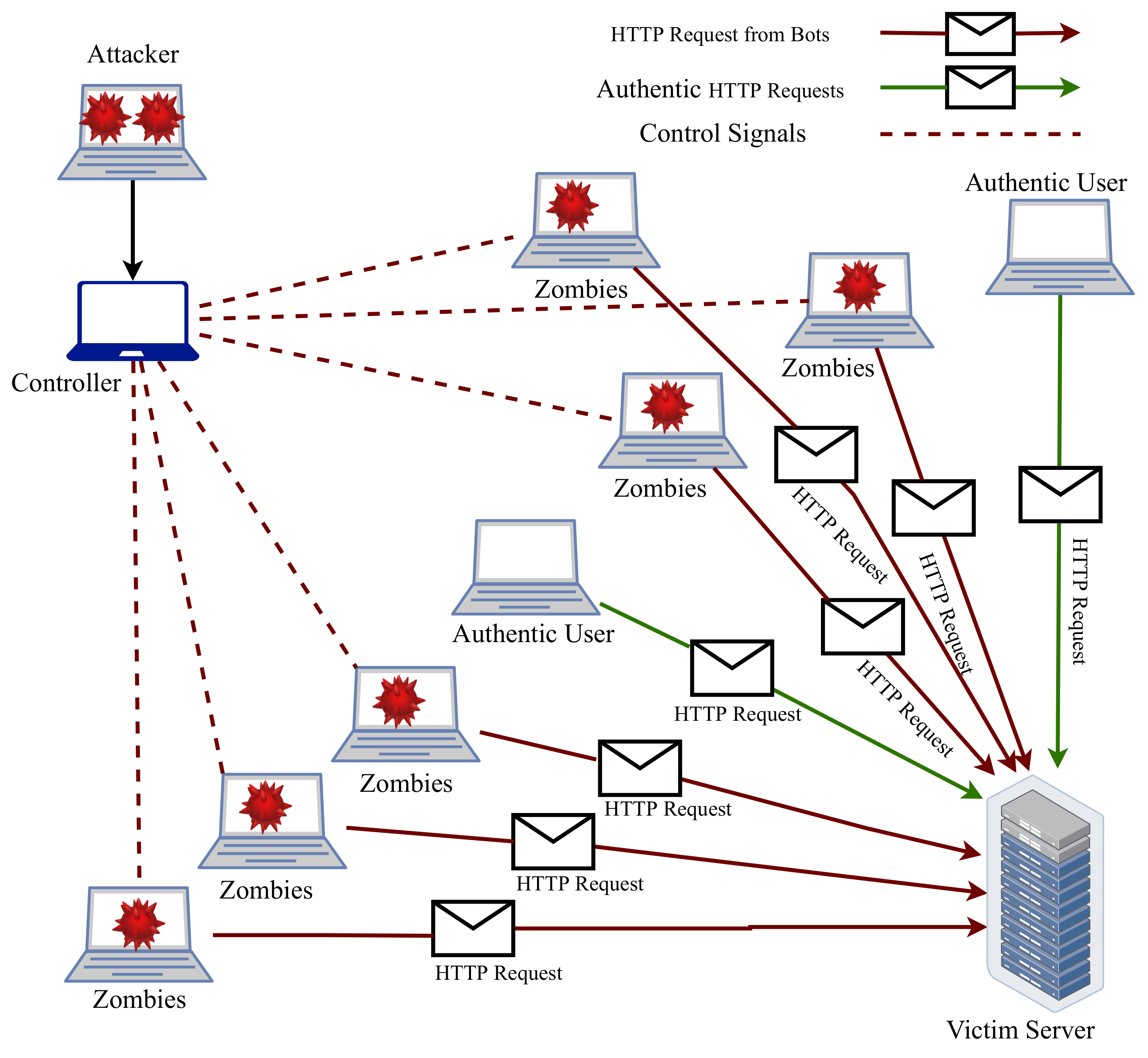
Denial of Service, is an attack that floods a network with traffic to overwhelm the network’s resources and prevent legitimate users from accessing resources on the network.
Attack Stages (Cyber Kill Chain)
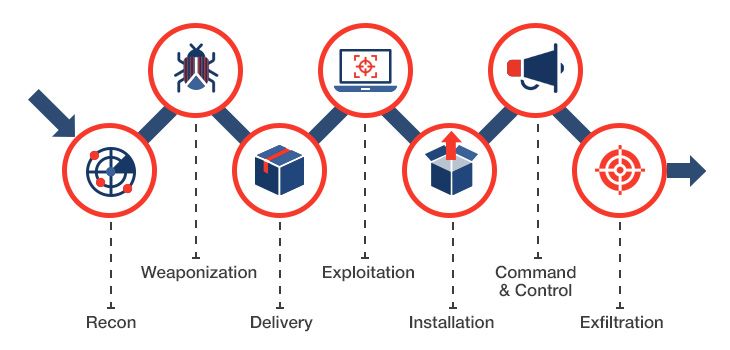
What is the Cyber Kill Chain?
- The Cyber Kill Chain is a model that was developed by Lockheed Martin back in 2011 with the purpose of helping organizations better understand the phases of various cyberattacks.
- However, while many may think this is simply a referential model, it’s one that can be used to identify at which stages a security team can prevent, detect, or intercept an attack in progress.
- Cyber Kill Chain is used as a reference, a way to better understand our adversaries, but it can be used as a guide for implementing better defenses as well.
- Not only does the Cyber Kill Chain lay out the anatomy of a cyberattack, it also highlights the increased level of impact an attack has as it progresses through each stage
Recon
This step involves passive scanning plus OSINT (i.e. social media, search engines, etc). It can also involve actively scanning public-facing IPs.
Weaponize
This is where the RAT (Remote Access Tool) is added to the exploit. The exploit can reside on a web page or a malicious macro-based document attached to an email. In this stage, the adversary also considers the method of delivery.
Deliver
This phase covers the delivery of the weaponized tool. The delivery method can be via email, social media, or a watering hole attack, to name a few.
Exploit
This phase is the actual exploitation. This is when a user opens the document attached to an email, clicks a link, etc. This can be a 2-step process where a loader is used to download the actual RAT. The loader will typically be small in size and reside only in memory.
Install
At this point, in most cases, additional tools are installed via the RAT. Other tools can be a network scanner, a keylogger, etc.
Command & Control
This is the command & control (C2) phase. This is when the victim’s machine will call out to an IP or domain and provide the adversary command-line access to the box.
Action
This is where the goal is achieved. The goal can be exfiltration.
This is when:
- The adversary scans the network, looks at/reviews data and grabs what they are looking for.
- What you’re protecting leaves the network.
Attackers Tools Vs Techniques
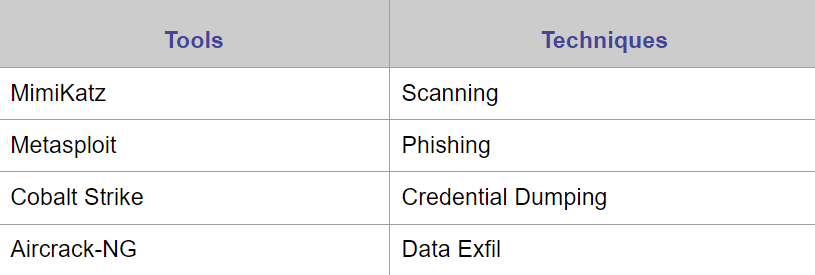
Red Team Solution ( MimiKatz - Metasploit - Cobalt Strike - Aircrack-NG )
APT Evolution
APT stands for Advanced Persistent Threat. It is a term used in the field of cybersecurity to describe a sophisticated and targeted cyber attack carried out by highly skilled adversaries. APTs are typically conducted by well-resourced threat actors, such as nation-states, organized crime groups, or advanced hacking groups.
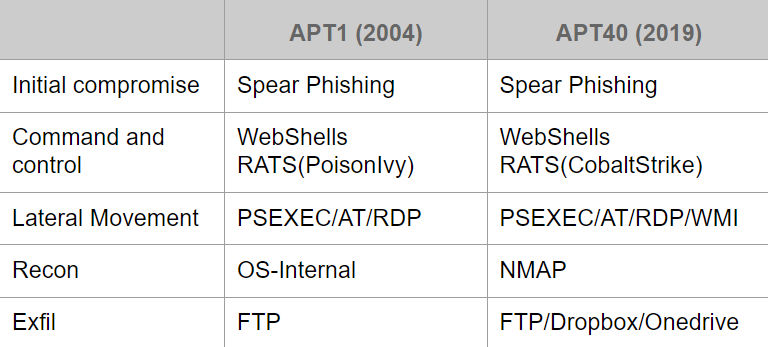
The primary goal of an APT attack is to gain unauthorized access to a targeted network or system and maintain a long-term presence without being detected. Unlike typical cyber attacks that aim for immediate gains or disruptions, APTs are characterized by their persistence and stealth. They are often carried out over an extended period, sometimes lasting months or even years.
Defense in Depth
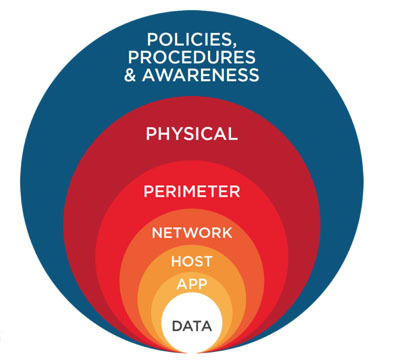
Defence in Depth is a concept used to describe a defence strategy in which security controls in multiple layers work together to form a single, cohesive security structure.
- Policies, Procedures, Awareness:
- Security Policies, processes, and procedures
- Awareness and training
- Physical Security:
- Gates, fences
- Badge readers, locks
- Closed Circuit Television (CCTV)
- Perimeter Security:
- Firewalls
- VPNs
- Network Security:
- Virtual local area networks (VLANs)
- Network intrusion detection/protection systems (NIDS/NIPS)
- Host Security:
- Antivirus
- Host-based intrusion detection/protection systems (HIDS/HIPS)
- Application Security:
- Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), Transport Layer Security (TLS)
- Data Security:
- Hashing, Encrypting
What is CVE?
Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) is a database of publicly disclosed information security issues. A CVE number uniquely identifies one vulnerability from the list. CVE provides a convenient, reliable way for vendors, enterprises, academics, and all other interested parties to exchange information about cyber security issues.
What is SOC?
A SOC is Security Operation Center,is a combination of people, processes and technology protecting the information systems of an organization through: proactive design and configuration, ongoing monitoring of system state, detection of unintended actions or undesirable state, and minimizing damage from unwanted effects

Cyber Defence
Cyber Defence provides the organization with foundational capabilities to detect, respond, and recover from cybersecurity incidents by identifying them in a timely manner, which reduces the impact to the organization. Cyber Defence efforts, while mostly technical in nature, require the ability to engage, collaborate with, and apprise leadership of incidents detected, the scope, and efforts being taken to contain and remediate.

Objectives OF Cyber Security Operations Center
- Log Collection, Log Aggregation, Security Analytics and Correlation.
- Building Threat Intelligence and Early Warning Detection System Incident Response Handling
- Monitors the Cyber Security posture and reports deficiencies
- Performs Threat and Vulnerability Analysis
- Provide Alerts and Notifications to General and Specific Threats
- Coordinates with regulatory bodies
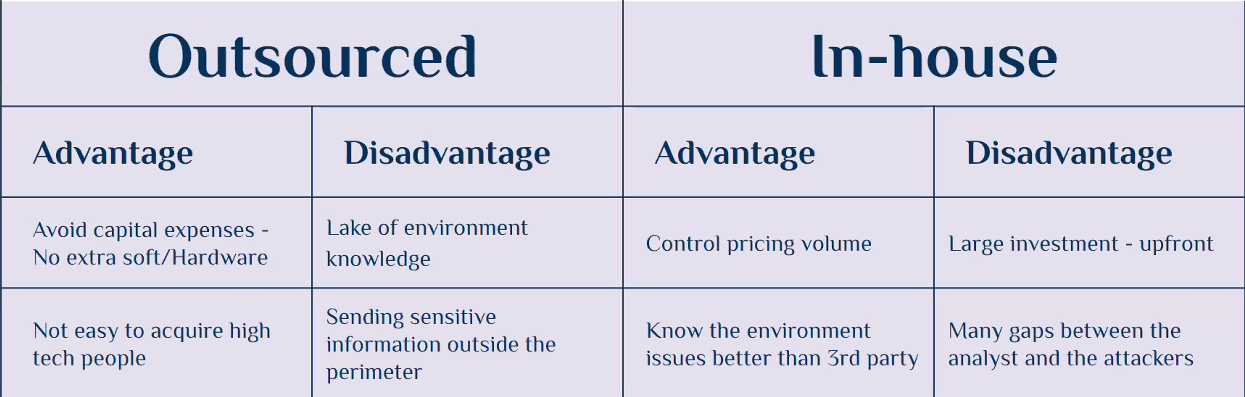
Outsourced or In-house
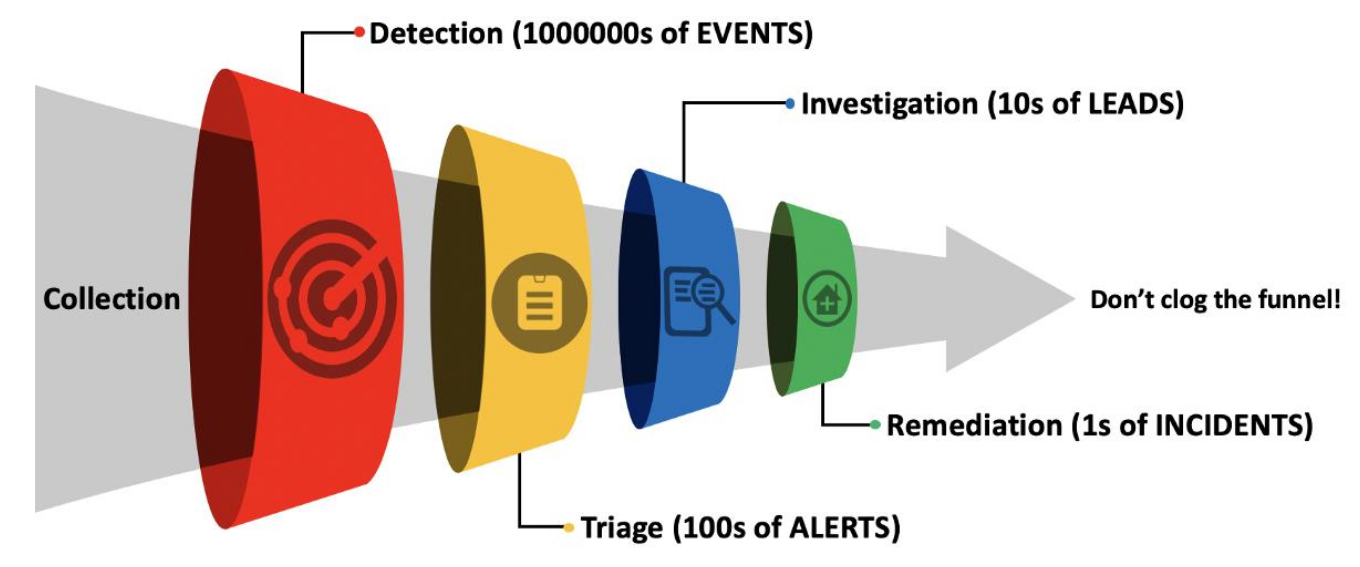
SOC Mission
Understand the SOC Environment
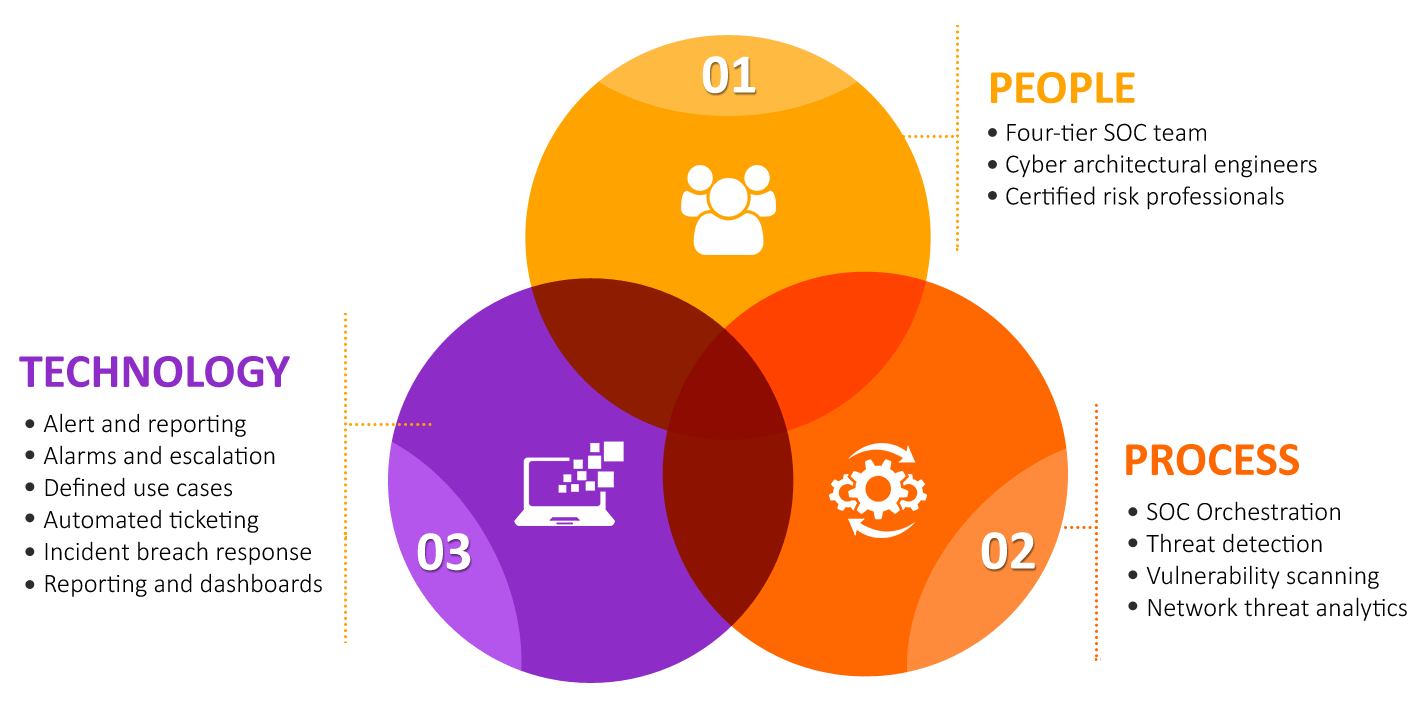
People
- mindset , burnout , building career
- The SoC crew should consist of people who are familiar with security alerts and threats and how to handle them, and also as security threats are constantly changing and evolving the SoC crew should be people who are willing to update their knowledge constantly.
Process
- Analysis, investigation theory, triage , escalation
- A professional SoC crew should have a standardized process of incident handling moving from tier 1 to 3 that ensures the effectiveness of the handling process.
Technology
- Protocols , SIEM , SOAR ,IMS , Detection Countermeasure
- A good SoC team should have an excellent toolkit of security audits and penetration testing tools and technologies such as Protocols, SIEM, SOAR, IMS, and Detection Countermeasures, updating your tools and following up with the recent security trends is needed with also the existence of a powerful documentation system to log incidents.
SOC Roles and duties
- Analyst
- SoC analysts are the first responders for any kind of cyberattack, their mission is to monitor, report, and implement powerful evasion techniques, they also do vulnerability analysis and product testing to identify any possible weaknesses and make suggestions based on their findings, they also have a major role in doing recovery plans and so on.
- SoC Admin
- SoC Lead
- The role of this position is to lead the rest of the team in their activities like monitoring, identification, and reporting.
- SoC Manager
- The SoC manager role is more comprehensive than the SoC lead as SoC managers manage the teams’ operations and provide technical guidance besides training and evaluation, SoC managers are also responsible for reporting incidents to the chief information security officer.
- Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI)
- Cyber threat intelligence is the skill of collecting information out of cyberspace that has been previously analyzed and shared between organizations about different attack scenarios and vectors.
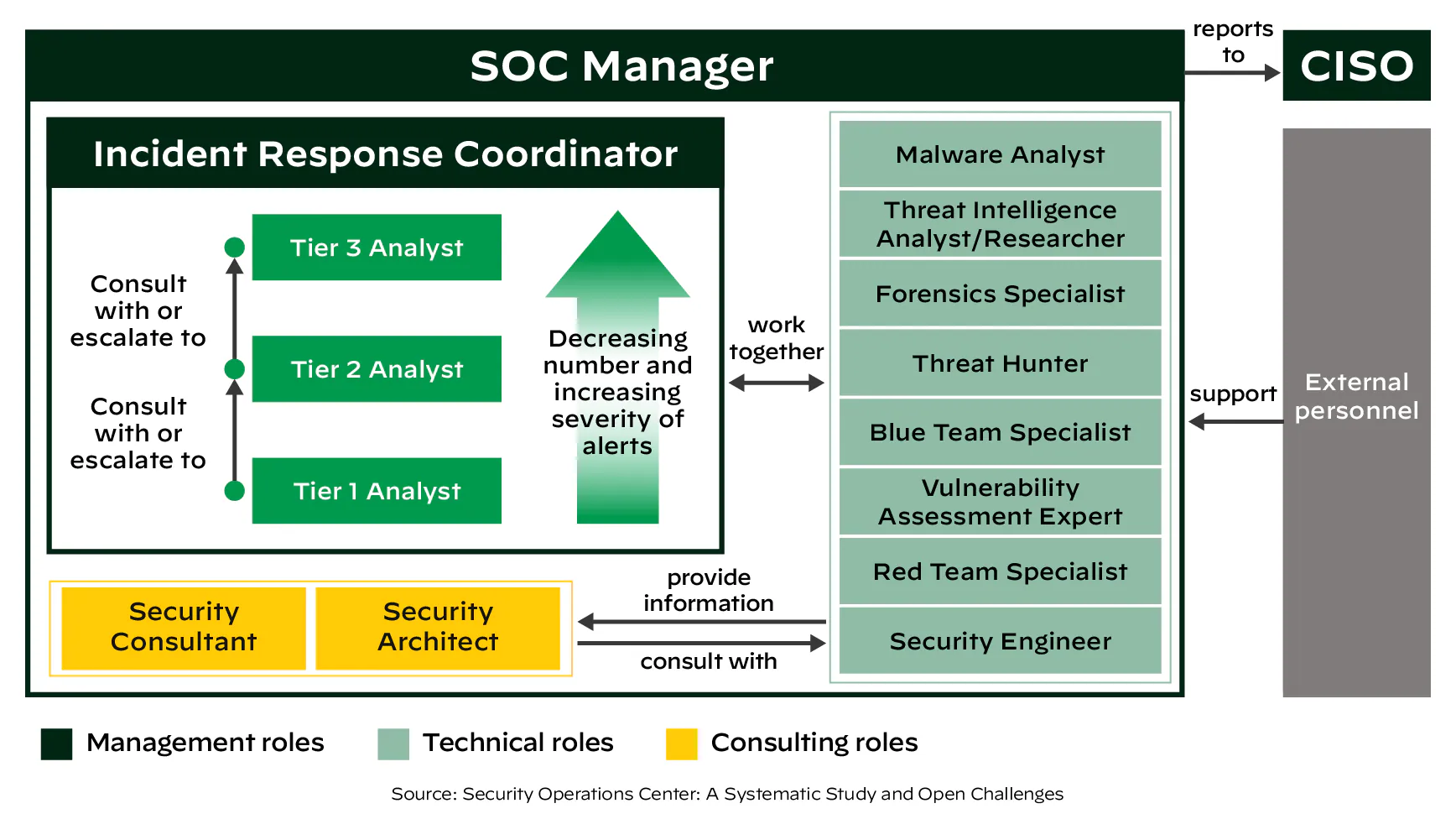
The SOC Team: Roles and Responsibilities
-
Tier 1 — Triage Specialist: Tier 1 analysts are mainly responsible for collecting raw data as well as reviewing alarms and alerts.
-
Tier 2 — Incident Responder: At the tier 2 level, analysts review the higher-priority security incidents escalated by triage specialists and do a more in-depth assessment using threat intelligence (indicators of compromise, updated rules, etc.).
-
Tier 3 — Threat Hunter: Tier 3 analysts are the most experienced workforce in a SOC. They handle major incidents escalated to them by the incident responders.
-
SOC Manager: SOC managers supervise the security operations team. They provide technical guidance if needed, but most importantly, they are in charge of adequately managing the team.
💡Useful Notes
Incident Classification
- A documented process or standard exists, based on organizational policy, that provides clear guidance on how to classify events and their associated responses.
- This standard is a core component of Incident Management that provides a sliding scale of engagement needs and asset allocations based on incident severity.
- This classification standard must closely align with business continuity and disaster recovery planning to provide sufficient oversight and executive awareness based on the organizational strategy.
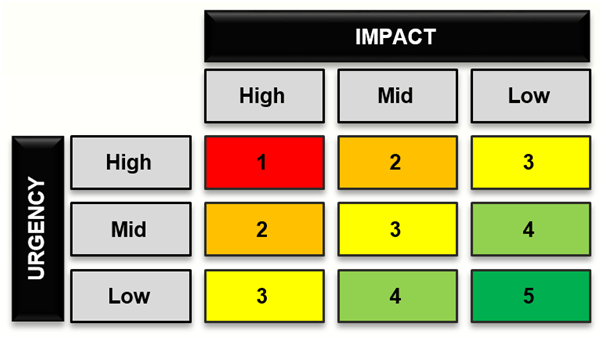
-
Impact – how critical the downtime is for the business. Usually, it is measured by the number of influenced users. If one or more services are down, the number can be determined from CMDB data or the service catalog.
-
Urgency – it is usually defined in SLA for the specific IT service. If more than one service is impacted, parameters for the higher urgency service will be taken into account.
SLA
Escalation Matrix
A documented process or standard exists, based on organizational policy, to document, manage, and publish a clearly defined escalation pathway with the associated authority for execution in the event of an incident. The escalation matrix must be understood by and centrally accessible to the workforce.
SOC Wiki
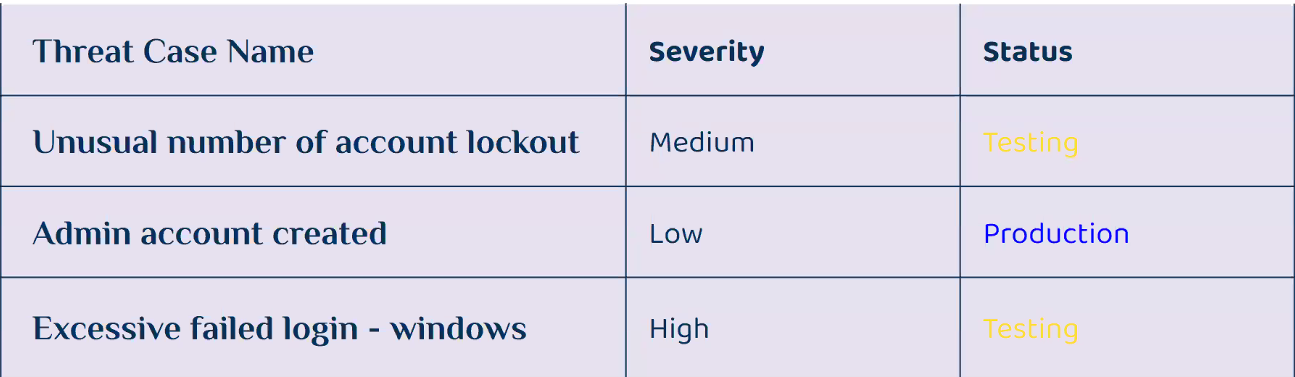
- Listed above is how Threat Cases are displayed in SOC-Wiki
- Threat Case Name, Severity, Status
- Information Centralized, Detailed and Searchable
- Information updated by SIEM and SOC Teams