Category: SOC - CyberTalents - Trend Micro - CTF
1. Competition
Q. Special kind of cybersecurity competition designed to challenge its participants to solve computer security problems
Flag
CTF2. CVE Number
Description
What is the CVE ID that is related to EternalBlue
Flag Format: XXX-XXXX-XXXX
Lets Solve This..!
What is EternalBlue?
EternalBlue is a Microsoft exploit which was used by the NSA in intelligence gathering operations. The exploit, officially named MS17-010 by Microsoft — gave the US National Security Agency (NSA) backend access to devices running Windows operating systems like Windows XP and Windows 7.
💡Do you know more about CVE check this Link or check this Link
Flag
CVE-2017-01443. Smart Role
Q. skills of collecting information out of cyberspace that has been previously analysed and shared between organisations about different attack scenarios and vectors.What is the role name of the above definition
Flag
flag{threat intelligence}4. Backdoor
Description
Our server compromised due to known vulnerability introduced from many years, Kindly check and identify this flow
X: Attack source → EX. “Internal/External”
Y: The Source IP → x.x.x.x
Z: CVE Num of the attack → xxx
W: Destination Mac Address
Flag format: flag{X:Y:Z:w}
Link: https://to-be-uploaded
Tools:
- Wireshark
🚩Challenge Link
🧑🏻💻Lets Solve This..!
let’s open the backdoor.pcap file with wireshark first, then lets show the Protocol Hierarchy Statistics and start first by filtering FTP traffic.
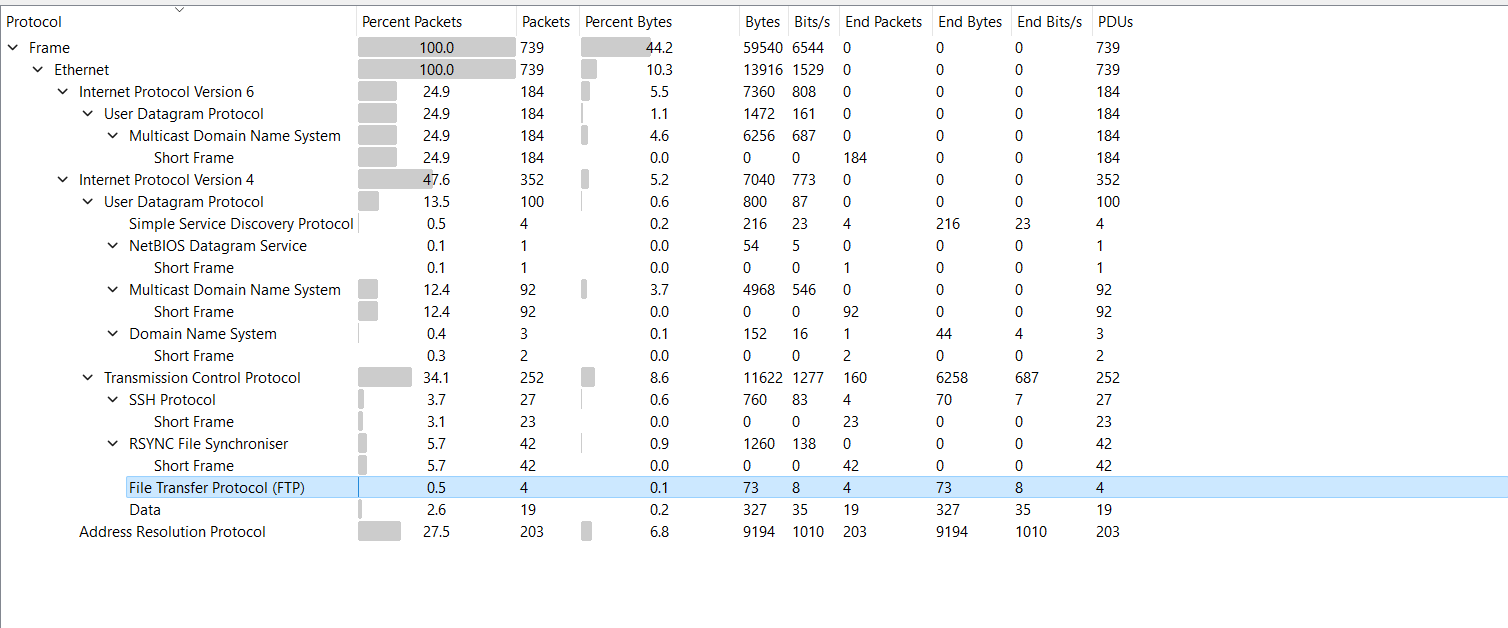
Filtering FTP traffic.
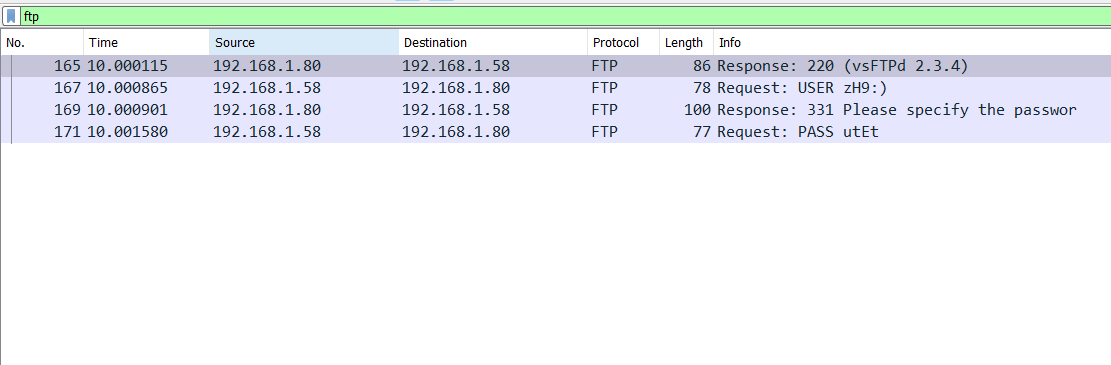
Selecting FTP protocol will generate search for subjected traffic and display fields like source, destination, destination port and info, From there we can see these traffic between two internal IP addresses
💡Wireshark provides the feature of reassembling a stream of plain text protocol packets into an easy-to-understand format.
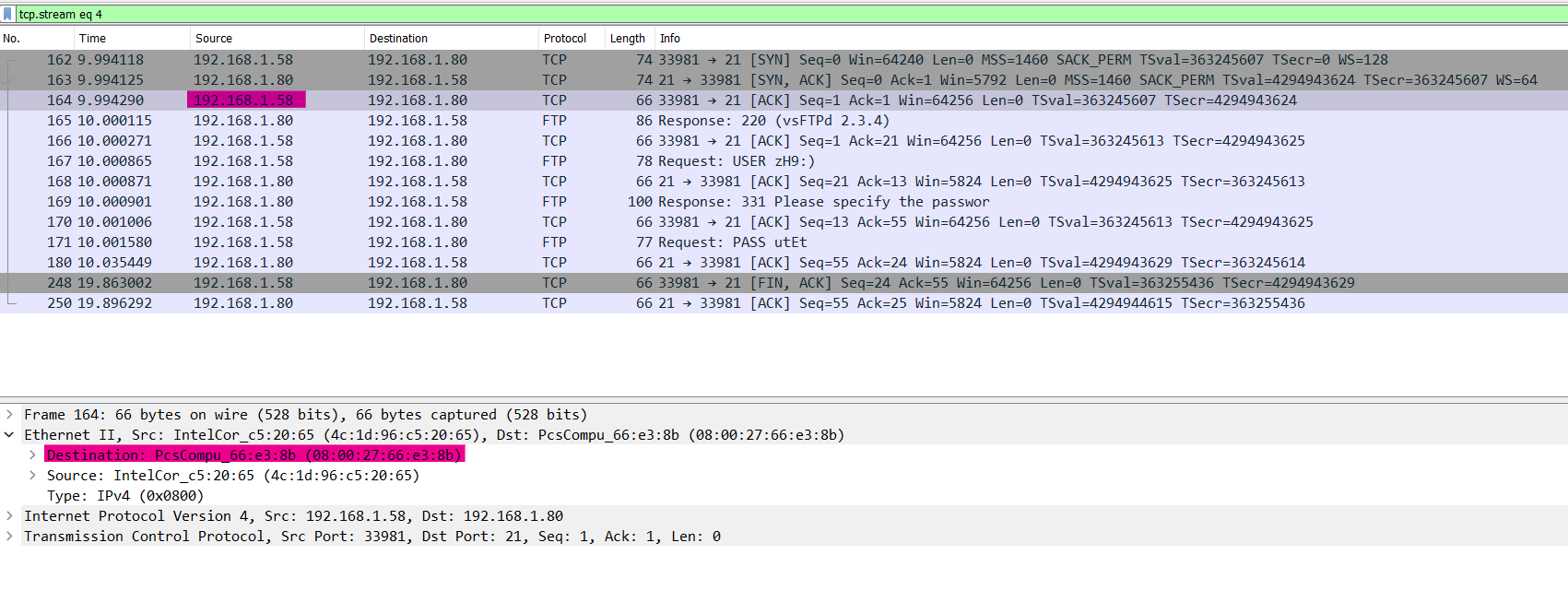
By selecting first packet (Right-Click) → Follow → TCP stream
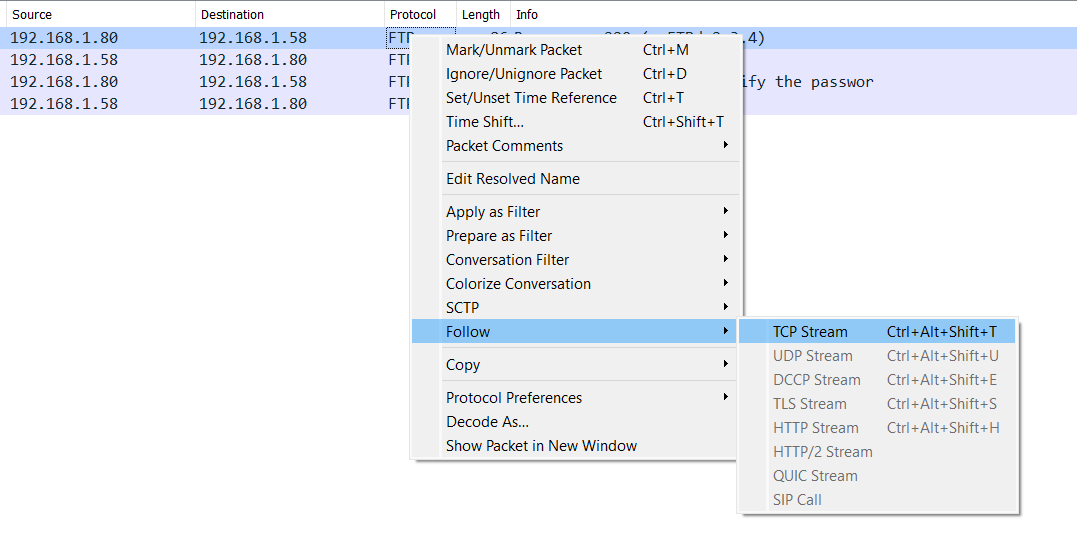
This is the result:
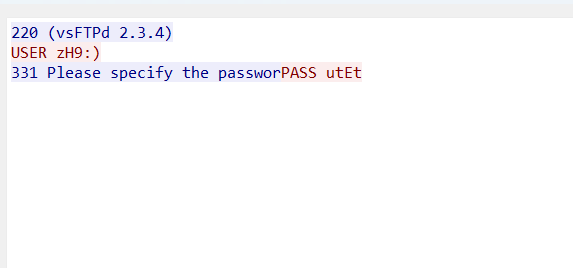
Here from the result we have useful information like:
- The FTP server receive the request from user and user name / password used for this authentication
Lets try to make this info useful 🤔
From the challenge description we know the the server is compromised by specific vulnerability and our task is to identify the root cause.
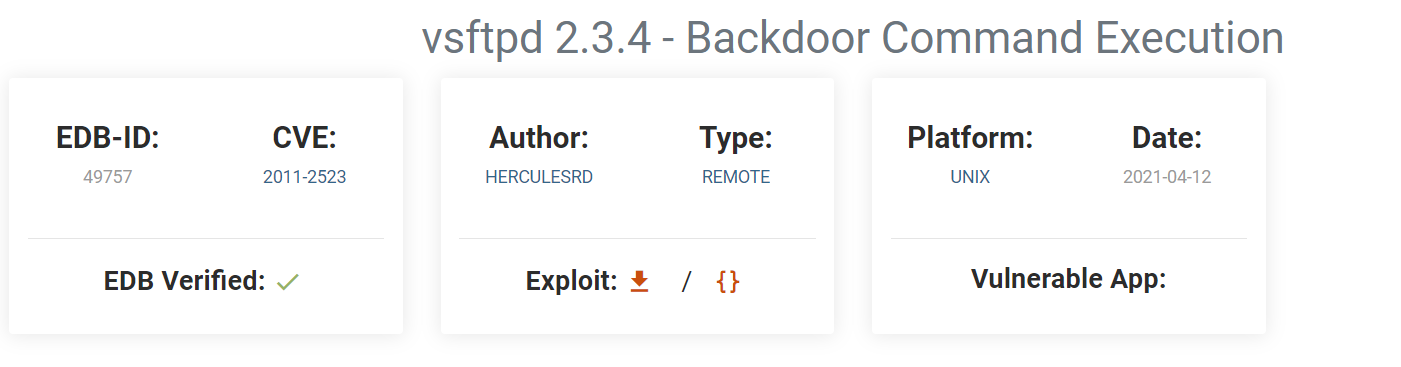
Googling the server version from the discovery result, we can notice its vulnerable to backdoor was introduced into the vsftpd-2.3.4.tar.gz archive.
Let’s search about this vsFTPd 2.3.4 vulnerability in Exploit DB
This is the result: vsftpd 2.3.4 - Backdoor Command Execution
Now lets try to cocatinating the flag:
- From PCAP analysis Both attacker and server have internal IP address in the range 192.168.1.0/24 So the attack scope is Internal this is the
Xportion - From PCAP analysis we can get the
Ypart that is the source IP of the attecker - Now we can get the
Zpart from the flag from aboveCVE ID - The last part of this flag
Wlets back to wireshark packets list to get the details, We could extract all Src/Dest network traffic details.
Flag
flag{internal:192.168.1.58:CVE-2011-2523:08:00:27:66:e3:8b}5. Creepy DNS
Description
Our NMS detect a suspected traffic, your task is to investigate the captured traffic and find the anomaly reason.
Tools:
- Wireshark
- Tshark
- CyberChef (Website)
🚩Challenge Link
🧑🏻💻Lets Solve This..!
let’s open the dns.pcapng file with wireshark first, then lets show the Protocol Hierarchy Statistics and start first by filtering DNS traffic.
Filtering DNS traffic.
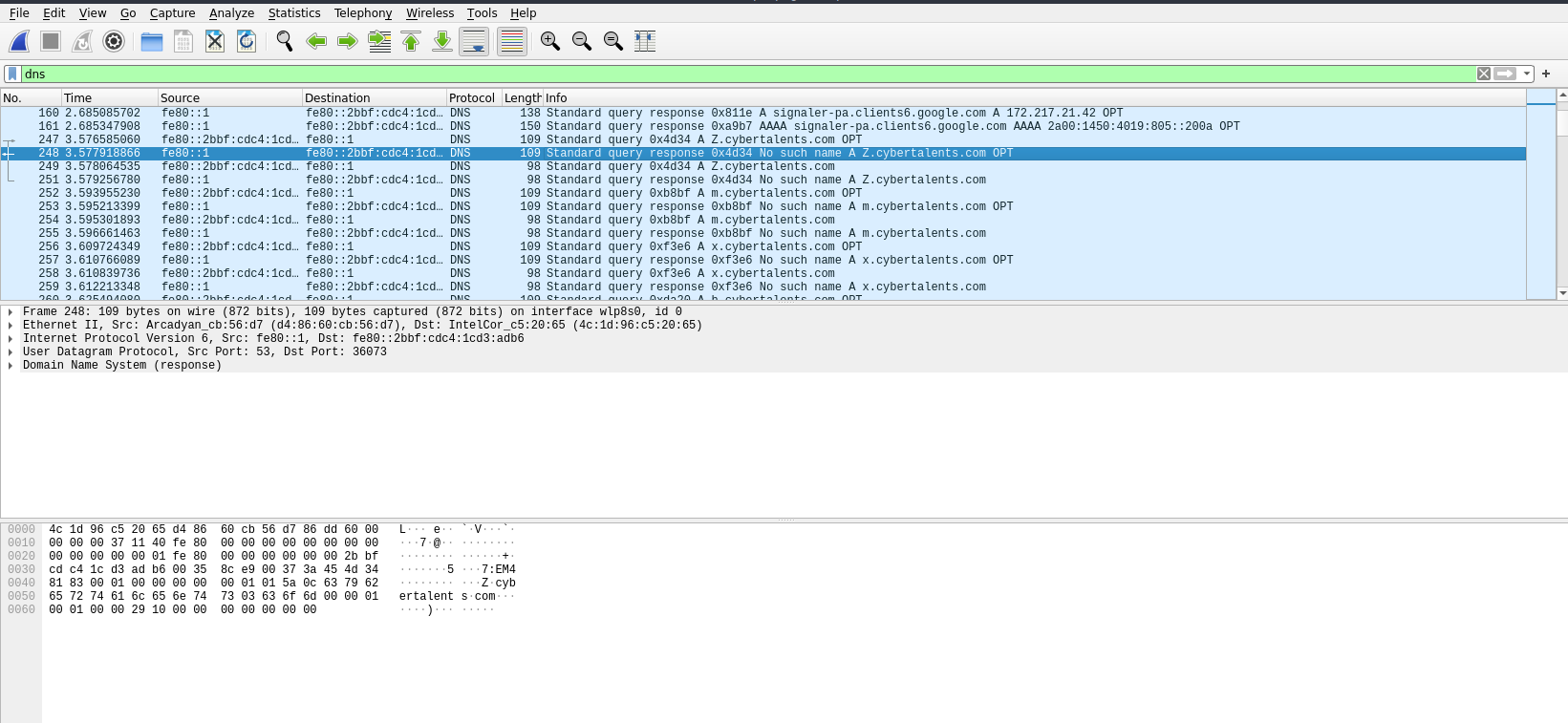
If we search through the traffic we can see at one point that there are many DNS requests to [x].cybertalents.com.
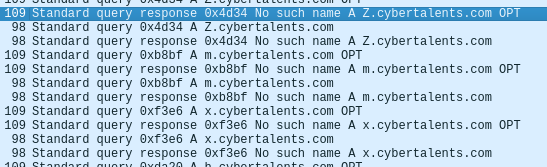
Let’s use Tshark to filter and collect all the letters.
tshark -r dns.pcapng -Y "dns.qry.type == 1" | grep 'cybertalents.com OPT' | cut -d 'A' -f 2 | uniq | cut -d '.' -f 1 | tr
- Dns.qry.type: filter only DNS requests (type ==1).
- The rest of the commands are bash tricks to sort the input.
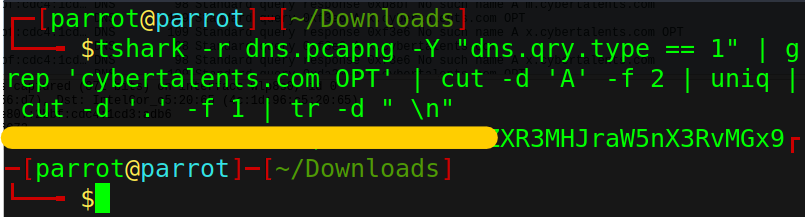
We got what seems like a flag encoded in base64.
Let’s Decode the string by using CyberChef
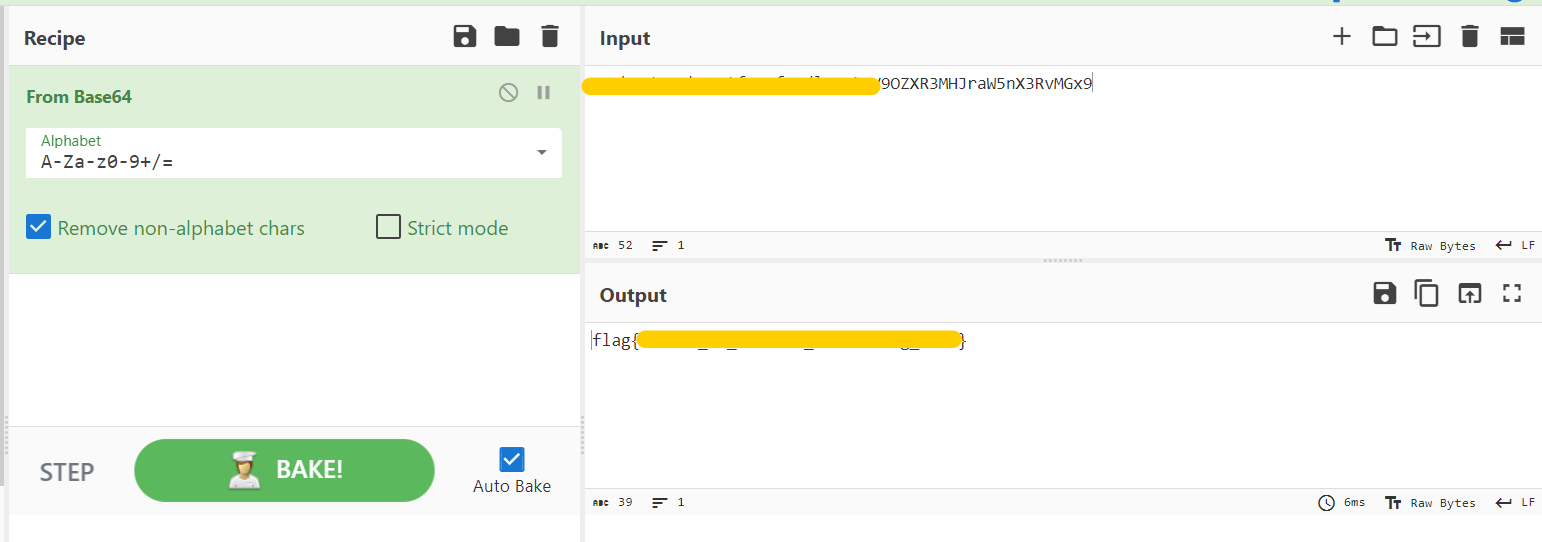
Flag
flag{tshArk_Is_Awes0me_Netw0rking_to0l}6. WormSeen
Description
OOur EDR has flagged suspicious traffic from production endpoint, after reviewing the respective process generating the traffic and another alert has been alerted “Worm Detected” in our SIEM
You decided to escalate the case to IR team to further investigate and answer the below questions
Questions:
- What is the range of worm spreading (x.x.x.x/xx) ?
- Destination target port of the attack (XX)?
- How many hosts might be affected by the worm (XX)?
- Flag format: flag{Answer1:Answer2:Answer3}.
Tools:
- Process Hacker
- wireshark
🚩Challenge Link
🧑🏻💻 Lets Solve This..!
Lets try to unzip the worm.zip in my isolated windows 10 machine, execute this file and show the result in Process Hacker tool.
Open Process Hacker after you run the worm.exe:
 |
|---|
| Screenshot for the execution of the .exe file |
Now lets look to Process Hacker and see if any change will be happend:
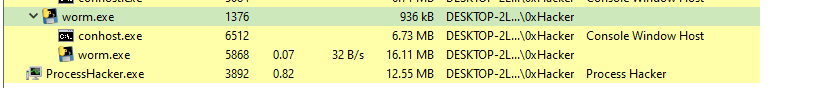 |
|---|
| worm.exe Process |
Then go to network tap to see the connection that the file make:
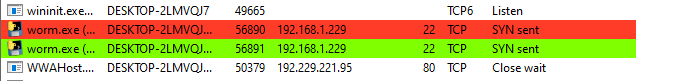 |
|---|
| worm.exe Network |
From above image after the file was executed it started to scan the network Lets open Wireshark to see the range of scaned network and answer the flag.!
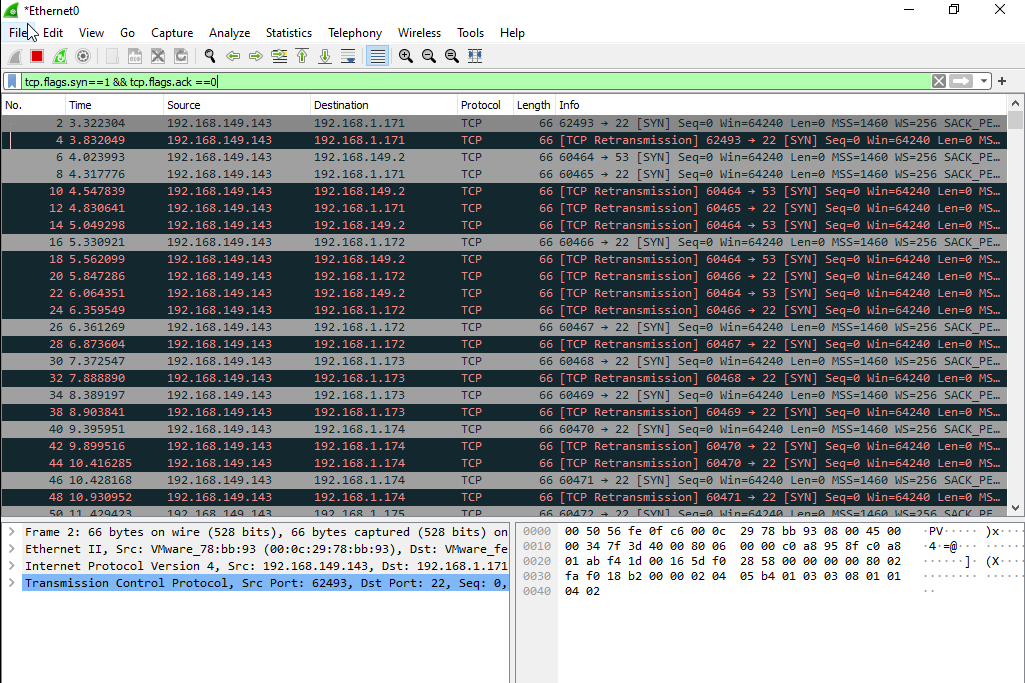 |
|---|
| Wireshark |
Now we want to know the range of ip address that the file scaned lets know from wireshark direct from first ip 192.168.1.171 and the last one 192.168.1.255
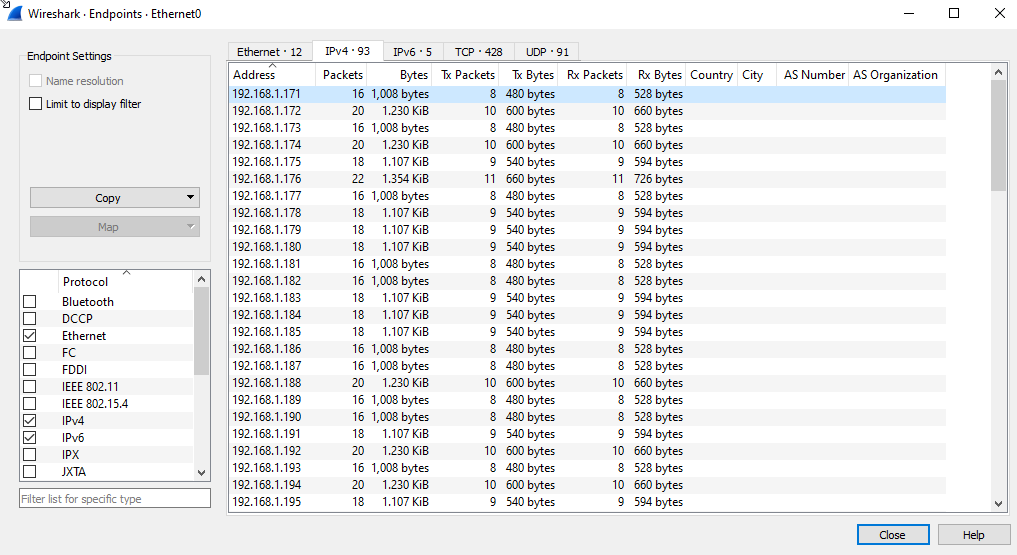 |
|---|
| Endpoint statistics |
Now concatenate all above answer to capture the flag..!
Flag
flag{192.168.1.0/24:22:85}7. Bean
Description
Come back home Mr. Bean.
Tools:
- dirsearch
🧑🏻💻 Lets Solve This..!
First install the dirsearch tool for directory brute forcing by using this command:
apt install dirsearch
Now lets open the URL in browser:
 |
|---|
| Come back home Mr. Bean. |
Second we use the dirsearch to scan the challenge url:
dirsearch -u <URL>
Result:
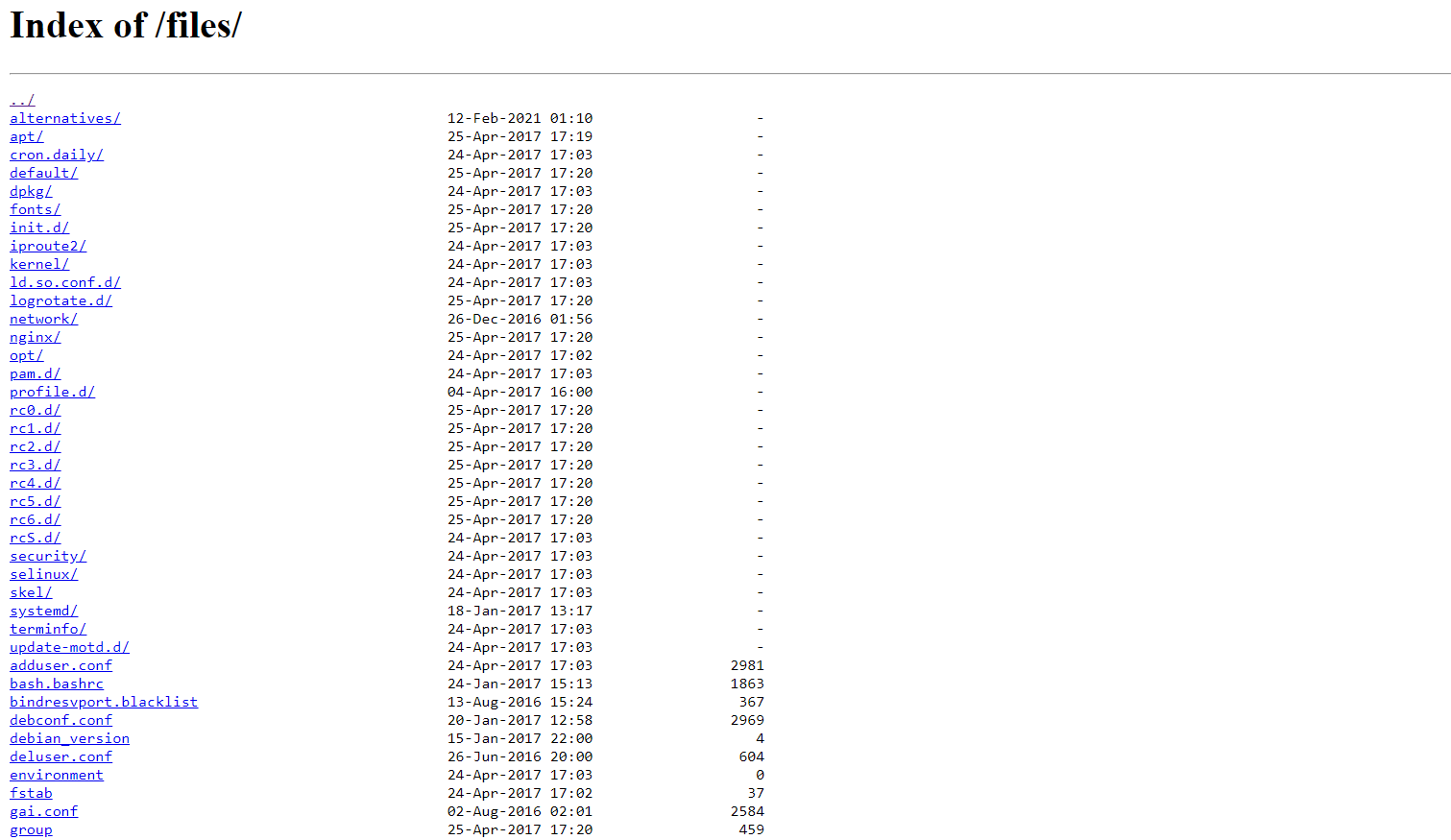
[13:14:29] Starting:
[13:15:27] 301 - 185B - /files -> http://*********-web.cybertalentslabs.com/files/
[13:15:28] 200 - 9KB - /files/
[13:15:31] 200 - 404B - /index.html
Lets try this directories in url:
 |
|---|
| Files |
From descrition line that tell us Come back home Mr. Bean.
Now we try go to the home directory of Mr. Bean and see the result using the url:
http://*********-web.cybertalentslabs.com/files/../home/
 |
|---|
| Files |
Woow! we find the flag.txt file lets open this file and summit the flag.
Flag
FLAG{Nginx_nOt_aLWays_sEcUre_bY_The_waY}8. Beans Detector
Description
You have received the alert in your company WAF that web attack happened recently. Please check and identify the below details
Follow the below Format in order to submit the flag:
- X: Attacker IP Address
- Y: Name of vulnerability scanner used by the attacker
- Z: number of bytes in the sensitive file leaked
- W: Date and time of the successful attack (xx/xx/xxxx:xx:xx:xx)
Flag Format: flag{X:Y:Z:W}
Tools:
- cat & grep commands
🚩Challenge Link
🧑🏻💻 Lets Solve This..!
Lets read the file content by using cat command and use my own filter on this file:
- X: Attacker IP Address
cat beansdetectorlogs | cut -d " " -f 1 | sort | uniq -c
41541 172.17.0.1
- Y: Name of vulnerability scanner used by the attacker
cat beansdetectorlogs | grep " 200"
172.17.0.1 - - [12/Jun/2022:11:04:06 +0000] "GET /index.html HTTP/1.1" 200 404 "-" "Wfuzz/2.2" "-"
- Z: number of bytes in the sensitive file leaked
- W: Date and time of the successful attack (xx/xx/xxxx:xx:xx:xx)
cat beansdetectorlogs | grep " 200"
172.17.0.1 - - [12/Jun/2022:11:05:12 +0000] "GET /files../home/flag.txt HTTP/1.1" 200 49 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Ubuntu; Linux x86_64; rv:95.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/95.0" "-"
Now concatenate all above answer to capture the flag..!
Flag
flag{172.17.0.1:Wfuzz:49:12/06/2022:11:05:12}9. Pass reset
Description
You have received the email below, Please examine the email and answer the below questions
Tools:
🚩Challenge Link
🧑🏻💻 Lets Solve This..!
11. SIEM Port
Description
Q. Your company planning to use Qradar as SIEM tool and you planning to receives logs from different different devices like routers, switches and some other devices, What Is The Default TLS Syslog Port That QRadar Listens On?
Flag
Protect Your Digital Presence & Stay Cyber Safe 💙
Thanks🌸