Category: SOC - CyberTalents - Trend Micro
Lesson 3: Introduction to Network Security
Network Fundamentals
Types of Networks
LAN:
- Also known as Local Area Networks, is a group of computers connected to each other locally or at one location.
WAN:
- Also known as Wide Area Networks, is a group of multiple LANs that has no limitations to city or country or else.
VPN:
- Also known as Virtual Private Networks, is a private network created over a public network and it creates an encrypted tunnel between network devices.
What is Network Security
Network security is the process of protecting and securing networks and underlying network infrastructure from different kinds of possible threats like unauthorized access, data disclosure, network destruction, and so on.
Network terminologies
IP Address
- IP is an acronym for Internet Protocol. An IP address is a unique address that identifies a computing device on the Internet or a local network.
Ports
- At the software level, the port is a logical construct used to uniquely identify a transaction over a network and the type of network service. Think of an IP address like the address to your house and ports as the doors.
Internet
- The Internet is a globally connected network of computing devices available to everyone for communication and sharing information.
Network Traffic
- Network traffic is the amount of data moving across a computer network at any given time.
Packets
- Packets are smaller units of data sent across a computer network.
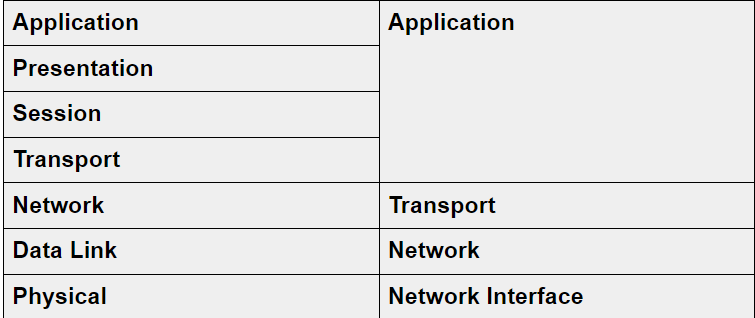
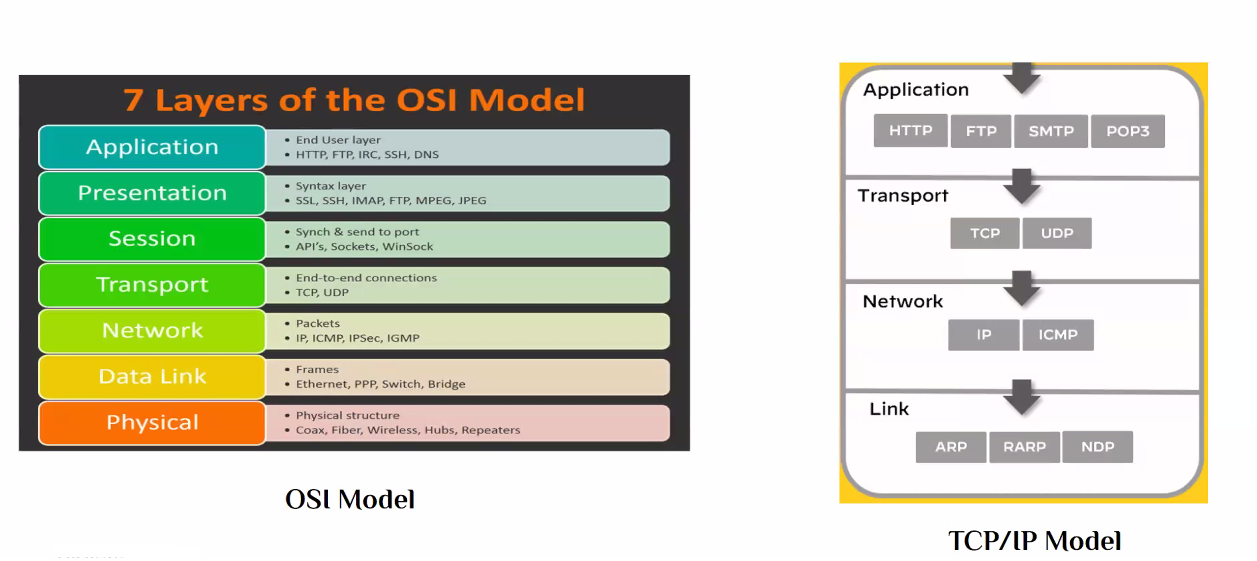
Network Models
- OSI and TCP/IP models are network communication models that are used to describe the function of a networking system and clarify the data transmission routine done in a network connection cycle.
The following is a table of the two models layers:
 |
|---|
| Network Models |
 |
|---|
| Network Models |
Important Network Protocols
Ethernet
- It is a LAN (local area network) technology protocol and it defines the physical layer of wired connection.
IP
- The internet protocol is a network layer protocol and it establishes internet connections through its routing functions.
TCP
- The transmission control protocol is a standard protocol that enables users to send and receive messages over the internet by defining the rules and layout of the transmission process and ensuring the integrity of the delivered data.
- Is a communication standard that allows computers to exchange messages and it is designed to guarantee the successful delivery.
UDP
- The user datagram protocol enables users to send and receive messages known as datagrams and it establishes a loss-tolerating speed connection.
- is also a communication standard but unlike TCP it is designed to ensure the quick delivery of the message not the integrity.
HTTP
- The Hypertext Transfer Protocol is a request-response type of protocol and it enables users to browse web resources and data. Most HTTP clients use TCP protocol in the connection process.
- Is a higher layer protocol that is used mainly to browse the web (the secure version: HTTPS).
ICMP
- It is used for error reporting and network diagnostics.
ARP
- It is a protocol used to discover or associate the IP address with the link layer address (MAC address).
SSH
- A communication protocol that enables computers to communicate over an secured channel.
SMTP
- Is a communication standard for mail transmission and is used by mail agents and servers.
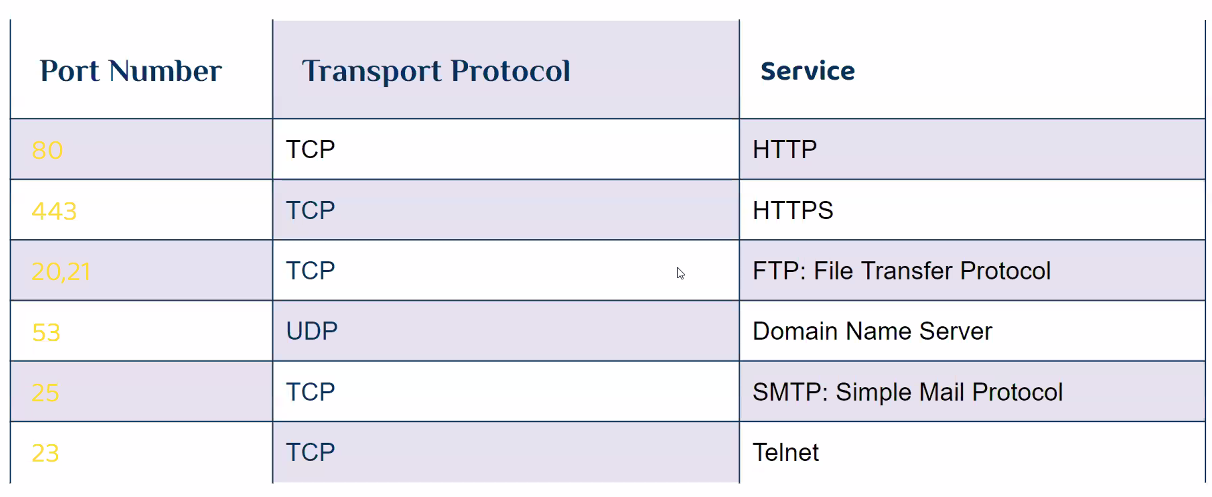
Common Ports & Services
 |
|---|
| Common Ports & Services |
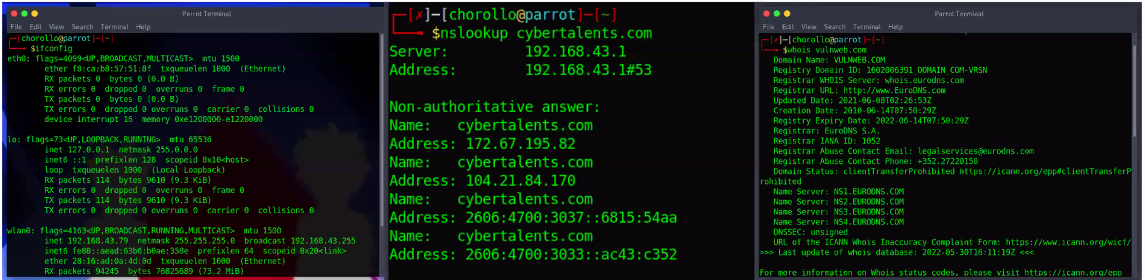
Important Networking Tools & Commands
- Ifconfig: this command is used to show the network interface configuration (ipconfig is the alternative in Windows).
- Ping: used to test for host capability to interact with another host.
- Nslookup: used for querying the domain name system.
- Netstat: display active connections (Windows).
- Whois: research domain and IP address information.
 |
|---|
| Important Networking Tools & Commands |
Network Security Protections
Access Control:
- The first step in network security implementations is to conduct a powerful access control mechanism for preventing unauthorized parts from accessing network resources and to manage the access level for employees in a suitable way.
Firewalls:
- Firewalls are a very common protection mechanism used in network security implementations, a firewall can be software or hardware.
- Firewalls are monitoring protections that monitor the income or outcome traffic, they can also filter data and isolate malicious traffic.
Firewalls Types:
- Stateful inspection firewalls.
- Packet filters firewalls.
- Application level firewalls (proxy).
Intrusion Prevention Systems:
- Also known as IPS. These are network security technologies that similarly to firewalls also monitor traffic and recognize exploits and prevent them.
Virtual Private Network (VPN):
- The VPN technology helps in establishing a secure tunneled private connection away from public internet networks.
- The VPN technology encrypts all the corporate network connections over the internet so the connection between employees’ devices and the network remains private.
Antivirus:
- An antivirus is a software that is used to detect and remove malicious software like viruses, worms, and trojans on network devices.
Lesson 4: Network Security Tools
Protect Your Digital Presence & Stay Cyber Safe 💙
Thanks🌸